What is docker?
Docker is a platform for developers and sysadmins to develop, deploy, and run applications with containers. The use of Linux containers to deploy applications is called containerization.
Containerization is increasingly popular because containers are:
- Flexible: Even the most complex applications can be containerized.
- Lightweight: Containers leverage and share the host kernel.
- Interchangeable: You can deploy updates and upgrades on-the-fly.
- Portable: You can build locally, deploy to the cloud, and run anywhere.
- Scalable: You can increase and automatically distribute container replicas.
- Stackable: You can stack services vertically and on-the-fly.
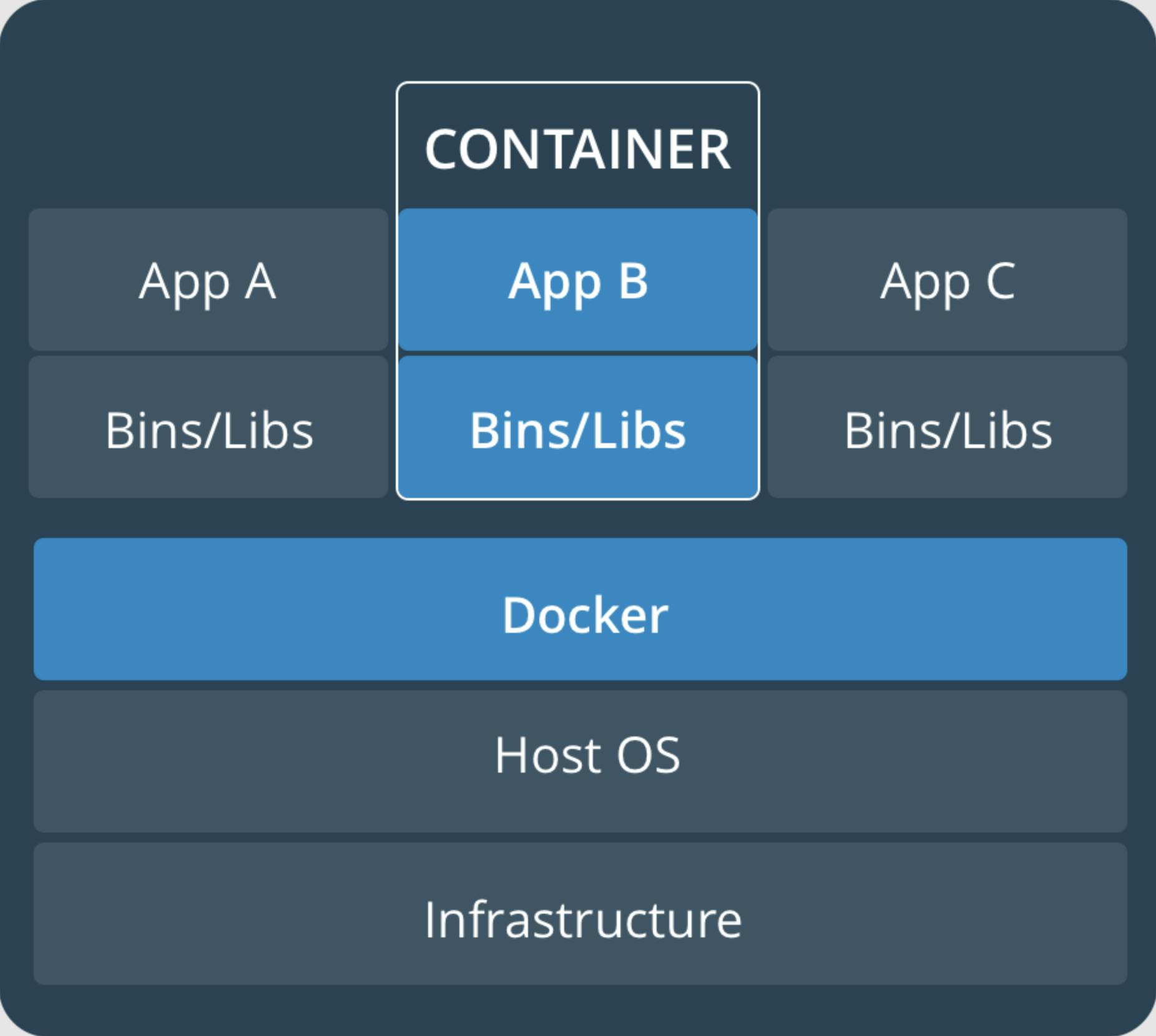
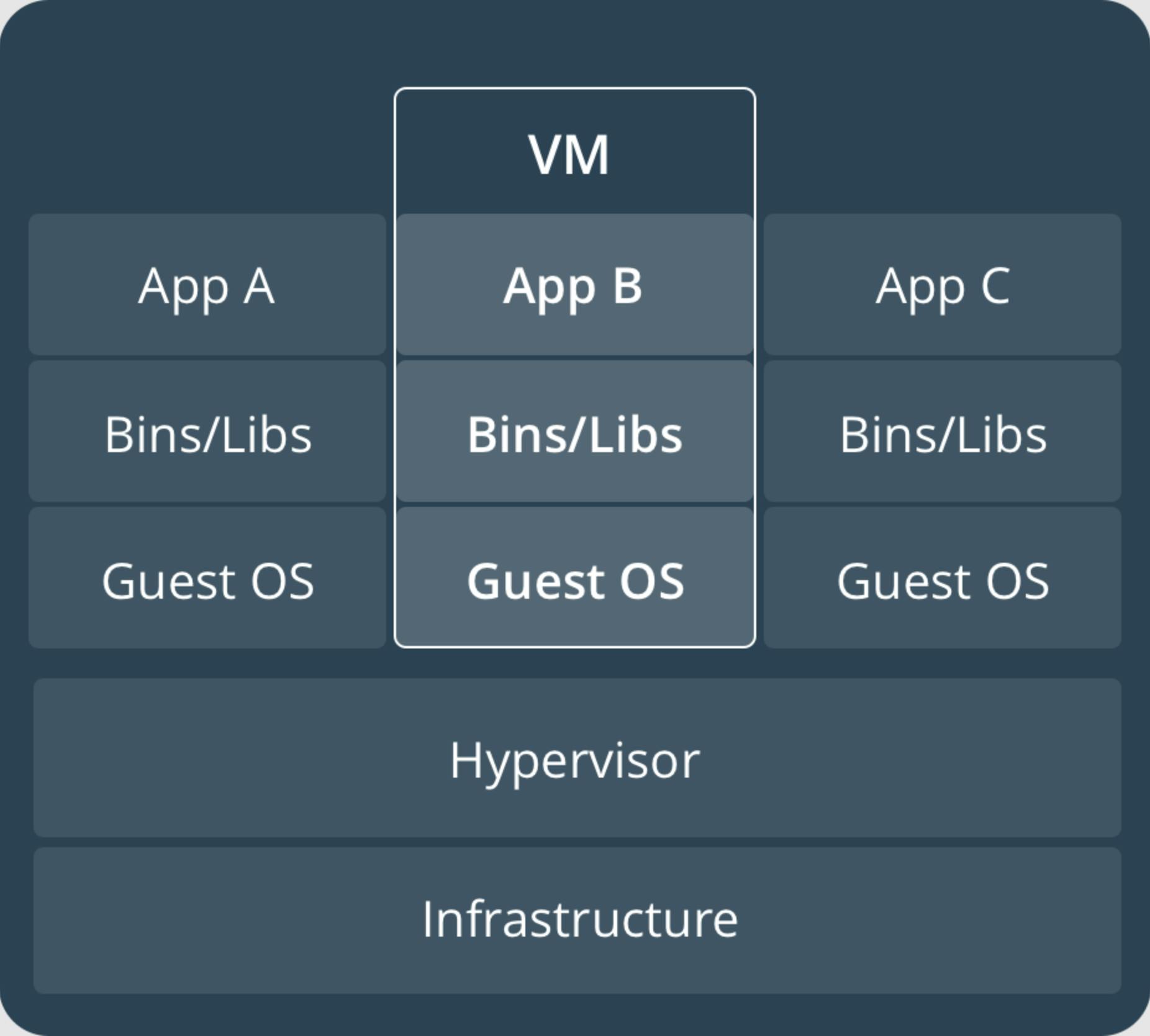
Containers VS Virtual Machines
A container runs natively on Linux and shares the kernel of the host machine with other containers. It runs a discrete process, taking no more memory than any other executable, making it lightweight. On the other side, a virtual machine (VM) runs a full-blown “guest” operating system with virtual access to host resources through a hypervisor. In general, VMs provide an environment with more resources than most applications need.
Cheat Sheet
## List Docker CLI commands
docker
docker container --help
## Display Docker version and info
docker --version
docker version
docker info
## Execute Docker image
docker run hello-world
## List Docker images
docker image ls
## List Docker containers (running, all, all in quiet mode)
docker container ls
docker container ls --all
docker container ls -aq
## Purging All Unused or Dangling Images, Containers, Volumes, and Networks
docker system prune -a
## Remove one or more specific images
docker images -a
## Remove dangling images
docker images purge
##Remove dangling volumes - Docker 1.9 and later
docker volume prune

